Ensuring transport accessibility of the population as an important area of \u200b\u200bsocio-economic development of the region. How to improve transport accessibility and improve the quality of transport infrastructure in Russia? Methods for increasing transport accessibility
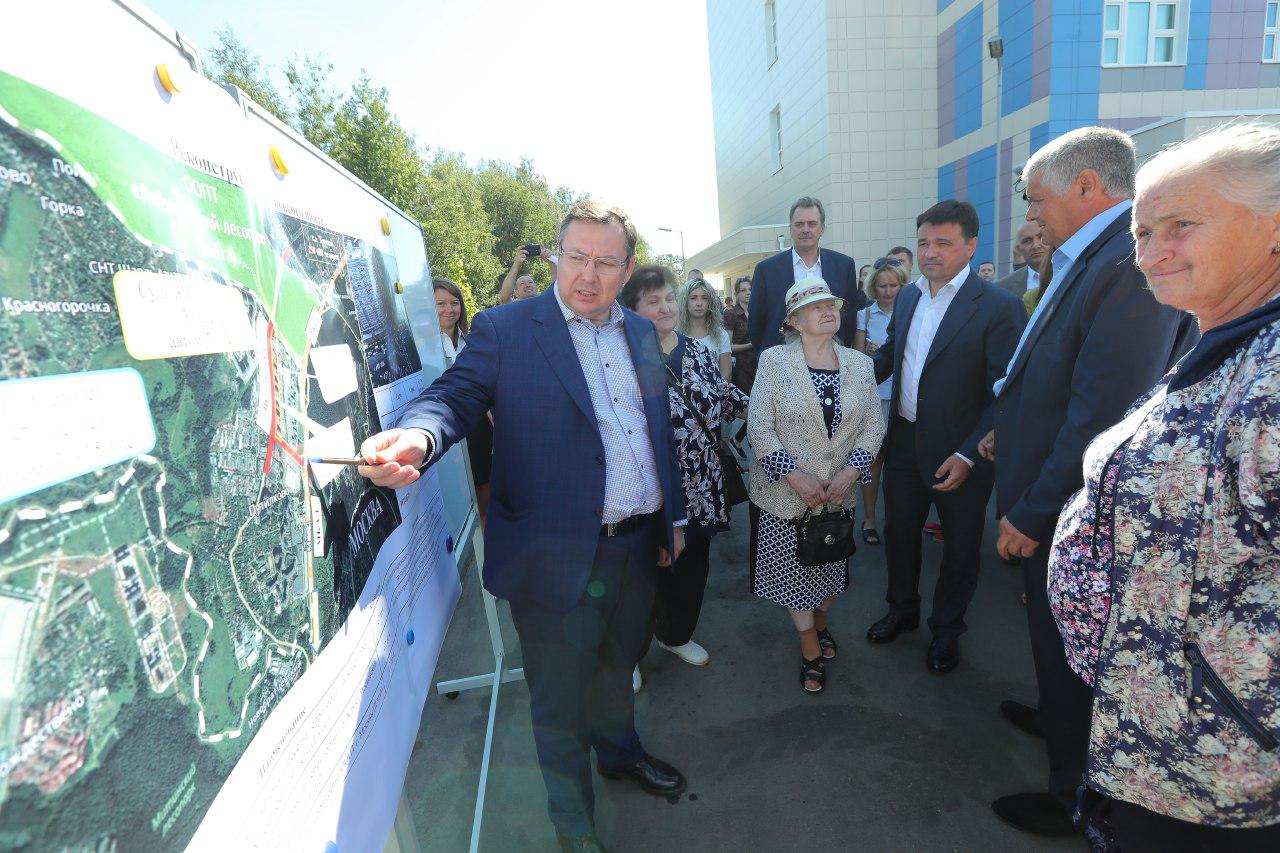
Reconstruction of the Putilkovskoye highway will begin in January 2019. This was reported to the Governor of the Moscow Region Andrei Vorobyov by the Minister of Transport and Road Infrastructure of the region Igor Treskov during a working visit of the head of the Moscow Region to the Krasnogorsk city district.
The length of the reconstructed object is 1.7 kilometers. At the moment, design and survey work has begun. The road is officially transferred from municipal ownership to the balance of the regional government. The cost of work will be 2.5 billion rubles. It is planned to complete the reconstruction in 2021.
“We gave in the design a reconstruction, expansion of the Putilkovskoye highway of the corresponding region. And in January-February, they should go to the construction site, prepare the territory and expand this road within 18-20 months, ”Andrei Vorobyov said.
 Photo source: press service of the governor and government of the Moscow Region
Photo source: press service of the governor and government of the Moscow Region During the reconstruction, the number of lanes will be increased to four. The expansion of the carriageway and the creation of new road infrastructure will significantly increase the capacity of the highway and improve the transport situation in the urban district.
 Photo source: 360 channel
Photo source: 360 channel In the village of Putilkovo completed the construction of a new school "Mosaic". It is designed for 1,510 seats. The Governor of the Moscow Region, Andrei Vorobiev, an educational institution and appreciated the quality of work.
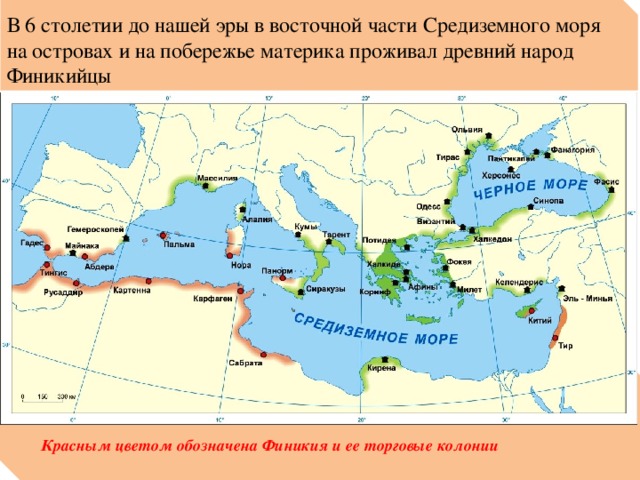
In the near future, it will be easiest to reach Moscow from Lyubertsy, Reutov, Mytishchi, Kotelnikov and Khimki, analysts at Metrium Group calculated. The rating of settlements was formed based on the calculation of the time spent on the road to the Moscow Ring Road. In addition, plans for the introduction of the underground and light metro, as well as the timing of the reconstruction of the main routes were taken into account. So,
now from Lyubertsy to MKAD can be reached in 10 minutes, taking into account traffic jams and in 7 minutes on a free highway, from Reutov - in 4 and 3 minutes, from Mytishchi - in 22 and 9 minutes, from Kotelnikov - in 14 and 8 minutes, from Khimki - in 10 and 6 minutes.
It is assumed that in Khimki, Mytishchi and Reutov, the underground metro will be introduced in 2015, in Lyubertsy - in 2017. The underground metro is planned in Lyubertsy (Nekrasovka, 2015), Kotelniki (Kotelniki, 2014) and Mytishchi (Chelobitevo, 2019).
However, a significant increase in prices caused directly by the improvement of transport infrastructure in these cities will not happen. According to experts interviewed by Gazeta.Ru, now the price increase in these cities is in line with general market trends. The increase in the cost of housing directly due to transport accessibility is hampered by frequent postponements in the construction of the metro, the active release of a new offer and fairly high housing prices due to proximity to the Moscow Ring Road. If we compare these cities as a whole with the suburbs, the level of prices for apartments in new buildings here will be approximately 10% higher. As a result, the cost per square meter in these cities is growing faster than in the suburbs. “They are adjacent to Moscow, so in any case, the demand for Lyubertsy, Khimki, Kotelniki is several times higher than in other remote areas,” said Daria Tretyakova, head of the consulting and analytics department at the ABC of Housing.
The highest price increases are usually due to the construction of the underground metro. However, in these cities, price increases based on the prospects for improving transport accessibility have, for the most part, already been won back. For example, according to estimates by the managing partner of Blackwood, a year and a half before the commissioning of the Novokosino and Lermontovsky Prospekt metro stations, apartment prices for individual residential projects increased by 30-35%. A similar situation in Lyubertsy - after the construction of the Zhulebino metro station and Lermontovsky Prospekt metro, the cost of housing has halved.
“In Lyubertsy, an active increase in prices came in 2012, when active work on the construction of the metro just began. As a result, over the year, prices for new buildings in the city grew by almost 13%, while in the near Moscow region as a whole, growth was about 3-5%.
At the same time, in 2013, price growth in the primary market of Lyubertsy amounted to about 7%, which corresponds to the average for the near zone of the Moscow Region. That is, improving transport accessibility has ceased to be an additional incentive for price increases, ”the head of IRN Consulting explained to Gazeta.ru.
The construction of a light metro affects the cost of housing less significantly.
“As for Reutov, Mytishchi and Khimki, it can be assumed that the local market for new buildings in these cities will react less actively to the commissioning of the underground metro
in comparison with the settlements where the classic metro should be held. This event can contribute to an increase in the cost of apartments in new buildings by 5-10%, but in the longer term, since the stations will appear only in 2015, ”says the CEO of Metrium Group.
Experts expect a more significant increase in housing prices in Kotelniki - however, due to other factors. Moreover, now the average cost of apartments here has slightly decreased as a result of the active release of new projects. “Within the framework of transport construction, in accordance with the city’s planning project, it is also planned to place a large transport hub near the metro. All this is likely to contribute to an intensive increase in prices for primary real estate, ”explains the Director General of Miel Newbuildings.
According to experts, in these cities now the growth in the cost per square meter is due to an increase in the stage of construction readiness of objects. Rising prices directly due to improved transport accessibility are expected in settlements farther from Moscow. “According to the project for the development of transport infrastructure in the Moscow region, a light metro will appear in Kryukovo, Sheremetyevsky, Pushkino, Zheleznodorozhny, Balashikha, Domodedovo, Podolsk, Odintsovo, Nakhabino, Vidnoye, Krasnogorsk. The cost per square meter of housing will increase more in those settlements where it was more difficult to get to the metro, ”says the director of the department of the MITs-Real Estate Presnya company.
Press services of the Mayor and the Government of Moscow. Denis Grishkin
The new passenger terminal of Aeroexpress opened at Paveletsky Station.
“Paveletsky transport hub is one of the most important in Moscow. Here passes more than 140 thousand passengers around the clock. An important element of this transport hub is, of course, the Aeroexpress terminal and the ability to get from Paveletsky Station to Domodedovo in a guaranteed 45 minutes, ”he said at the opening ceremony.
He added that the terminal's throughput has increased almost three times. In addition, it is well integrated with the Paveletskaya metro station: “Additional elevators, escalators have been built, there is the possibility of a transfer from the metro to the express train, and the passage from the metro to the terminal has almost halved. I hope that the number of passengers after the opening of the terminal will increase. ”
As specified by the Deputy Mayor of Moscow in the Moscow Government, the head Maxim Liksutov, Paveletsky Station is one of the largest transport hubs in the capital. “Five different modes of transport are here. This is the metro, it is a suburban railway, it is long-distance passengers, it is a bus service. There is a tram nearby and, of course, an aeroexpress train, ”he said.
More than five million passengers
Aeroexpress has been transporting passengers between Paveletsky Train Station and Domodedovo Airport since 2008.
Currently, 36.5 pairs of trains per day run along the route. Driving time is from 06:00 to 00:30. Travel time is 45 minutes.
Since the beginning of 2015, the company transported 5.4 million passengers, i.e. 19 percent of the airport’s passenger flow, in the direction Paveletsky Station - Domodedovo Airport.
The creation of the new Aeroexpress passenger terminal at the Paveletsky railway station is a joint project of the company and Russian Railways. It will increase the comfort of passenger service and enhance the benefits of Aeroexpress over alternative travel routes to Domodedovo.
The Moscow government supports this project: it is fully consistent with the city’s plans to create comfortable transportation hubs for passengers of public transport.
Passenger Area Expansion
Repair and reconstruction of the premises of the Paveletsky station, necessary for the creation of a new terminal, was carried out as soon as possible - from September to December 2015. As a result, the passenger area of \u200b\u200bthe terminal increased 2.5 times - from 750 to two thousand square meters. In the waiting room appeared 125 seats for passengers.
There were also more ticket offices: there were three before, now five. Ticket offices are equipped with special devices for hearing impaired passengers. One of the cash desks was adapted for people with limited mobility.
In addition, the following work here:
- 16 ticket machines for Aeroexpress;
- information desk;
- ticket validation kiosk;
- Three kiosks for self-registration of passengers on flights;
- monitors with Aeroexpress train timetables and flights at Domodedovo airport;
- Racks for charging mobile devices;
- free Wi-Fi;
- pharmacy;
- ATMs;
- the shops.
In the waiting room, personal assistants work - employees of the Aeroexpress company. They help to get tickets and accompany the visually impaired and low mobility passengers to trains.
“It is very important that the terminal fully meets all the requirements of FIFA, since in 2018 the World Cup matches will be held in Moscow. All the requirements put forward by our colleagues from FIFA are fully met here, and the terminal is ready to receive fans, football players, all those who want to attend the World Cup in 2018, ”the deputy mayor emphasized.
The path to the subway has become shorter
The most important part of the reconstruction was the closer integration of the terminal with the metro station Paveletskaya. As a result of installing three elevators and increasing the number of escalators from three to five, you can get from the metro station to the Aeroexpress trains twice as fast. A more convenient connection with suburban trains of the Paveletsky direction also appeared.
The new terminal is adapted for passengers with reduced mobility. The terminal's capacity has increased three times - up to 1800-2000 passengers per hour.
The project to create a new terminal was funded by Russian Railways and Aeroexpress.
Improving transport accessibility of Domodedovo
One of the objectives of the development program of the Moscow transport hub is to improve the transport accessibility of Domodedovo Airport.
The Moscow Government has reconstructed the Warsaw and Kashirsky Highways connecting the airport with the city center. In fact, the reconstruction of the transport interchange of the Kashirskoye Highway and the Moscow Ring Road was completed.
Rosavtodor built a junction on the 43rd kilometer of the highway to the airport (turn to the Aviation Village).
Also completing the construction of an additional second main track on the site Domodedovo (Aviation) - Domodedovo Airport. This will make it possible to schedule an additional four pairs of Aeroexpress trains.
Station improvements and infrastructure upgrades
Suburban and urban rail transport the Government of Moscow considers as one of the most important and promising elements of public transport.
In 2014, the volume of passenger traffic through the Moscow railway junction amounted to 680 million people, which is 40 percent more than in 2010 (480 million passengers). The Moscow railway junction accounts for more than 50 percent of all suburban transportation in Russia.
The program for the development of passenger infrastructure at the railway junction provides for the construction of 240 kilometers of additional main tracks, the purchase of new-generation railcars, and the reconstruction of stations and platforms.
As part of the implementation of this program, in 2011-2015, we reconstructed and improved the stations and station squares, and put things in order on passenger platforms. In the planned mode, rolling stock is being updated: outdated trains are being replaced with modern comfortable trains.
Passenger traffic was opened on the Novo-Peredelkino-Kievsky station section, as well as along the fourth main route of the Oktyabrskaya Railway on the Moscow-Kryukovo section. This improved the transport accessibility of Zelenograd and Khimki.
The reconstruction of the Small Ring of the Moscow Railway to organize passenger traffic is nearing completion. In the radial directions, work is underway to modernize the infrastructure. On the Yaroslavl, Gorky, Kursk directions of the Moscow Railway, additional main routes are being built to increase the volume of suburban transportation.
In particular, construction is underway in the Yaroslavl direction:
- the fifth main route in the sections of the Yaroslavsky railway station - Losinoostrovskaya and Losinoostrovskaya - Mytishchi;
- the fourth main route on the Mytishchi - Pushkino section;
- The third main route on the Mytishchi-Bolshevo section.
Work is underway in the Gorky direction:
- on the fourth main route in the Kurskaya-Passenger - Railway section;
At the Reutovo-Balashikha overpass.
In the Kursk direction:
- construction of the third and fourth main routes Moscow-Passenger-Kurskaya - Lublino;
- reconstruction of the Lyublino - Podolsk line.
Rolling stock update
In 2015, the Governments of Moscow and the Moscow Region held a competition for the choice of carriers that will serve suburban rail transport for 15 years. A long-term agreement will allow the formation of infrastructure development and rolling stock renewal programs.
The winners of the competition were the existing carriers - OJSC Central PPK (nine directions) and OJSC Moscow-Tver PPK (October direction).
During the implementation of the railway infrastructure development program, they will purchase at least 1880 new, modern wagons for suburban electric trains.
At the same time, Aeroexpress won the competition for the selection of a carrier on routes connecting Moscow with the airports of the Moscow Aviation Hub. Thanks to a long-term contract, the company will continue the construction and reconstruction of terminals.
“The meaning of the contract for 15 years is that the company got the opportunity and commitment to invest funds for 15 years in order to improve the passenger service infrastructure of Moscow and the Moscow transport hub every year. Colleagues said that about 20 billion rubles will be invested over the next 15 years in updating both rolling stock and passenger infrastructure, ”said Maxim Liksutov.
Bulletin of Omsk University. Series "Economics". 2012. No. 1. S. 40-46.
INCREASING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF THE PROCESS OF FORMING ACCESSIBLE TRANSPORT INFRASTRUCTURE IN THE REGIONS
INCREASE OF EFFICIENCY OF PROCESS OF FORMATION OF AN ACCESSIBLE TRANSPORT INFRASTRUCTURE IN REGIONS
K.E. Safronov K.E. Safronov
Siberian State Automobile and Highway Academy (SibADI)
The program-targeted approach to the formation of a barrier-free environment for people with limited mobility in a regional aspect is presented. The formation of an accessible environment is considered as an intensive way of economic development and an effective way of investing. It is proposed to study this problem comprehensively in the "housing - environment - transport - service facilities" system and solve it using modern project management methods.
In article the program-target approach to formation of the accessible environment for people with the limited possibilities in regional aspect is considered environments. Availability - the public blessing, which utility is especially effectively shown on a labor market and in social sphere. Formation of the accessible environment is an intensive way of development of economy and an effective way of an investment of investments. The "habitation-environment - transport - objects of service" is expedient to consider the given problem in a complex in system and to solve modern methods of management of the projects.
Key words: barrier-free environment, transport accessibility, people with limited mobility, project management, investment, economic efficiency.
Key words: accessible environment, transport availability, people with the limited possibilities, project management, investments, economic efficiency.
Recently, more and more attention has been paid to the accessibility of the living environment for people with limited mobility (MGN). In our country, the implementation of the state program “Accessible Environment” for 2011-2015 has begun, the purpose of which is to create conditions by 2015 to ensure equal access for disabled people, on an equal basis with others, to the physical environment, transport, information and communication, as well as to facilities and services open or provided to the public. The total funding for the program for 2011-2015. will amount to 46.9 billion rubles., Including 26.9 billion rubles. from the federal budget, 19.7 billion rubles.
From the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, from extrabudgetary sources, it is necessary to attract 269.3 million rubles. . The main condition for the implementation of departmental and regional target programs is the organization and conduct of their competitive selection. The size of the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation should be at least 50% of the amount of funds provided for this purpose at the expense of the federal budget.
The infrastructure of most regions of our country is not adapted for living, moving and servicing MGN, which include: hearing and vision impaired people with impaired musculoskeletal system and their accompanying persons, senior citizens, children, pregnant women, as well as people with active lifestyles and traveling with prams, with luggage, on bicycles and rollers, etc. Now, according to the Ministry of Health and Social Development, 13.2 million people with disabilities live in Russia, 66% of them are pensioners and 4% are children. Only 26% of disabled people of working age work, 60% of people with disabilities of the musculoskeletal system face barriers in using public transport, 48% experience problems buying food. A third of the population suffers from inaccessibility of the environment. All civilized countries are on the path to integrating people with disabilities into society, this is provided for by the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, which has already been signed by 147 countries, including Russia.
© K.E. Safronov, 2012
The needs for the formation of affordable transport infrastructure in our country have ripened long ago and are formulated as follows:
People with disabilities and MGN due to the inaccessibility of the environment are limited in the exercise of their constitutional rights;
Restrictions for a significant part of the population of the living environment has negative social and economic consequences for the whole society;
The level of economic development of Russia allows you to direct part of the funds to the formation of a barrier-free environment;
An accessible environment, including transport infrastructure, contributes to the innovative development of the economy.
The resources that the public sector receives by accumulating the revenues of the state and municipal budgets are realized in the form of public expenditures, which is understood as the use of resources in order to satisfy the needs for public goods and implement social redistribution processes. Sometimes the market mechanism does not allow for the achievement of a paired retroactive allocation of resources. For a number of reasons, situations may arise that are called market failures in which the market does not cope with its functions, either cannot ensure the production of goods at all, or cannot ensure its production in an effective volume. It is precisely this inability of the market to provide access to
stupidity, despite the laws adopted, can be considered as the basis for state intervention in the economy. There must come an understanding of the competitive advantages that accessibility gives, so that this mechanism works at its full potential.
The main target setting of state budget policy is to improve the life of the population. For its implementation, it is important to concentrate sufficient budget expenditures in priority areas and sectors that can strengthen economic potential and at the same time increase budget revenues. One of the mechanisms for allocating and redistributing public goods is program-targeted budget planning. The effectiveness of its implementation depends on the quality of the development of the target program. In this regard, studies aimed at developing regional programs on accessibility of the environment and transport infrastructure, determining the amount of funding and socio-economic efficiency of programs are becoming particularly relevant.
Methodology for the formation of affordable transport infrastructure. Since 2004, SibADI has been conducting research on the organization of transport services for disabled people. During this time, a methodology has been formed for the formation of an accessible transport infrastructure (TI), based on the program-targeted approach and the project management method (Project management) and including an economic assessment of accessibility (Fig.).
1. Identification of problems of accessibility of TI
2. Transforming problems into goals
3. Development of investment projects for the availability of TI
Scientific and Methodological Financial
Urban Transport
Legal Technical
Social Organizational
Economic Information
Investment Environmental
4. TI Availability Audit
Odds
availability
6. Development of a target program; 5. The rationale for the costs of collateral
Examination and approval of accessibility of TI
7. Preparation of tender documentation 8. Implementation of investment projects
Tenders for the availability of TI
10. Assessment of the effectiveness of investment; 9. Formation of a project team;
tony Control accessibility projects; Control
Methodology for creating an affordable transport infrastructure
Consider the individual points of this methodology in the context of the development of regional accessibility programs.
1. The development of regional and municipal accessibility programs begins with the identification of problems. The tools here are sociological surveys, field surveys (audits) and analysis of the impact of accessibility on the social and economic development of society. Identification of transport accessibility problems is based on an analysis of the process of movement of people with disabilities. Such movements are carried out in the environment of life: "housing - environment - transport infrastructure - objects of gravity", which includes individual elements of service systems. Each element of the system has a set of indicators characterizing its availability: biases, dimensions, dimensions, distances, time, safety, cost, efficiency. In most cases, a certain level of transport service system (municipal, regional, federal) is involved. The degree of realization of the needs of MGN depends on the state of its availability. An analysis of the accessibility of transport infrastructure in large cities of the Russian Federation revealed problems that need to be addressed.
Scientific and methodological problems are associated with the lack of a methodology for creating an accessible transport infrastructure and evaluating its effectiveness. Not enough attention is paid to conducting research and training. Accessibility measures are not always laid at the stage of infrastructure design, which increases costs and reduces their effectiveness.
Urban problems are related to the fact that housing, the urban environment, transport and social infrastructure are not adapted for the movement of MGN. All this takes a lot of time, effort and means of transportation, leads to excessive mileage of vehicles, overloading the road network and environmental degradation. Sections of urban planning documentation on accessibility are formal in nature and are not always implemented, the novelty of the subject and the lack of a training system are responsible.
Legal problems in many regions are associated with gaps in the legislative and regulatory framework and the lack of expertise on accessibility. Transport infrastructure facilities often give up with violations of accessibility requirements.
Social problems. Disability is not an attribute of the person himself, transport inaccessibility forms the socio-environmental component of disability and leads to technological discrimination of persons with disabilities. This also includes medical and educational problems: the former are associated with difficulties in the rehabilitation of persons with disabilities, and the latter are associated with their training and integration into society.
Economic problems. The inaccessibility of transport infrastructure for people with disabilities and MNG causes significant economic damage associated with the action of numerous negative factors. Inaccessibility of a business significantly affects its attendance and profitability. Low mobility creates unemployment and poverty among people with disabilities, and for the state - an increase in social spending. Inaccessibility holds back consumer spending, which affects the economy. This problem concerns not only people with disabilities and their families, but also the economic and social development of the whole society, where human potential remains unclaimed, which ultimately affects GDP growth.
Investment problems. To obtain a reliable assessment of the effectiveness of investments in the development of the transport complex, the availability factor must be taken into account. There is no mechanism for stimulating state and non-state structures to intensify activities in terms of ensuring conditions for the accessibility of social and transport infrastructure for people with disabilities and people with limited mobility.
Funding Issues. The lack and irregularity of funding leads to the fact that work on the construction and reconstruction of transport (social, engineering) infrastructure is carried out in a limited time and with low quality. Practice shows that the main criterion for competitive selections is the low bid price that negatively affects the quality and set of consumer properties of the final product.
Transport problems are associated with the lack of an established system of transport services for the disabled. The forms of transport services are considered: individual transport, pedestrian traffic, social taxi, urban and extra-urban passenger transport, the functioning of specialized routes.
Technical problems are related to the lag of the rehabilitation industry. There are no standard solutions to access issues.
the number of objects of social and transport infrastructures, rolling stock. Innovative technologies are slowly being introduced into the passenger transportation process.
Organizational problems are associated with the absence in most regions of a management system for the formation of accessible transport infrastructure. When solving accessibility issues, project management methods are not used, and the operational activities of administrative structures are not focused on solving complex problems. In addition, such structures, due to the novelty of the topic, have not yet been created.
Information problems are associated with the lack of a database on the accessibility of transport infrastructure, there is no register of wheelchair users. There are no indicators in the statistical accounting system that reflect the availability of housing, social and transport infrastructures for MGN. A system of objective criteria and methods for conducting an audit of accessibility for disabled people of buildings and structures, means of transport, communications and information, relevant design and technical documentation, instructions and the procedure for its implementation has not been developed.
Environmental problems are associated with excessive mileage of vehicles, obsolete rolling stock, congestion in the street-road network and an increase in harmful emissions caused by the underdevelopment and inaccessibility of pedestrian and transport routes.
2. These problems by the project management methodology are transformed into goals and objectives and are solved at the modern scientific level using domestic and foreign experience. Approaches to solving the problems include:
The development of a new scientific direction “accessibility economics”, which examines the impact of accessibility on the development of the economy;
Implementation of the whole complex of measures to form a barrier-free environment, including training personnel, using the principles of universal design and sections on accessibility in urban planning documentation;
Improving the regulatory framework at the federal, regional and municipal levels;
Providing disabled people with equal access to prestigious values \u200b\u200bin this society: to receive educational, medical, social and other social services, decent work;
Determination of damage from inaccessibility of transport infrastructure and justification of costs for accessibility measures;
Development of investment projects using the mechanism of public-private partnership and assessment of their socio-economic efficiency;
Identification of motivation and incentive measures for the implementation of accessibility measures, the creation of a mechanism for their sustainable financing;
Increasing the mobility of the population by organizing transport services for people with disabilities and IH with the choice of forms of TOI, adaptation of the route network and rolling stock
Development of the production base of means of accessibility and rehabilitation, modernization of the rolling stock of passenger transport;
Organization of databases on the accessibility of transport infrastructure for MGN;
Formation of an effective management system for the development of transport infrastructure taking into account accessibility
Increasing the accessibility of the pedestrian and transport network, which will reduce the mileage of vehicles, unload the road network and reduce the amount of harmful emissions;
Using an integrated approach to the rehabilitation of people with disabilities, which consists of three components: medical, social and labor.
Currently, rehabilitation is considered not only as a system of measures of specific areas, but also as a process of changes in the state of the disabled. The most promising way to integrate people with disabilities into society is social rehabilitation, which is customary to consider through social and cultural inclusion and an independent lifestyle, in which a barrier-free environment and accessible transport play an important role.
3. A barrier-free environment is a public good that improves the quality of life of the entire population. According to the functional classification of state budget expenditures, accessibility refers to expenditures on social policy, transport, road facilities, communications, and computer science and is an expenditure obligation of the state. The development of investment projects for accessibility has a number of features. The obligation to create favorable conditions for people with disabilities extends to organizations, regardless of their form of ownership, so investors who want to improve
sew the availability of your business. In any case, the development of accessibility projects begins with an assessment of the existing availability situation.
4. In SibADI, a universal
the methodology for conducting an audit of the accessibility of various objects, which includes: selecting an object for inspection, selecting the composition of the commission, compiling a list of regulatory requirements, verifying their compliance and developing measures to address them. We have developed a system of coefficients that reflect the availability of various elements of the living environment for people with limited mobility: 0
Availability not required; 0,1 ... 1 - not available; 1,1__2 - available with extraneous
power; 2.1.3 - available independently. The advantages of such a system lies in the transition from expert assessments to specific indicators that allow us to analyze, systematize and improve accessibility. These criteria can be used in the statistical accounting system.
5. In many regions, targeted programs are already being implemented to create a barrier-free environment, adopted on the basis of the Federal Target Program "Social Support for Persons with Disabilities for 2006-2010." Their analysis showed a wide range of funding volumes. It is possible to assess the financial possibilities of the regions when financing targeted programs on the basis of their cost in relation to the regional GRP and per 1 resident. Fluctuations are significant: from
0.02% (Samara region) to 2.12% (Lipetsk region). In terms of specific indicators, the values \u200b\u200balso vary: 3495.3 rubles. for 1 resident (Moscow) and 2025.6 rubles. (Omsk region).
Difficulties in developing regional and municipal targeted programs based on the GP “Accessible Environment” for 2011-2015. are financial and technical in nature. Despite the fact that this procedure is prescribed by federal law, in some regions there are still no regional norms that determine the procedure for the development and adoption of targeted programs.
6. In the Omsk region, a long-term target program “Accessible Environment” for 2011-2015 was developed. with funding of 2.4 billion rubles. The program measures are aimed at creating accessibility of social, engineering and transport infrastructure for people with disabilities, which will help to overcome the self-isolation of people with disabilities, increase their individual mobility and social activity, create conditions
to lead an independent lifestyle. The program measures were developed on the basis of a comprehensive analysis of the situation of people with disabilities in the Omsk region, identifying existing restrictions and barriers to the accessibility of the living environment for people with disabilities, and their impact on the socio-economic development of the Omsk region. The program-targeted method will allow more efficient use of financial resources, concentrating them on solving priority problems, providing a comprehensive solution to the problems identified by this program.
Within the framework of the “Ensuring unhindered access for disabled people to social, engineering and transport infrastructure” activities, measures will be taken to implement the principles of universal design, primarily at the main objects of social infrastructure, to adapt buildings, premises, and adjacent territories for disabled people. This will create conditions that provide the indicated categories of the population with equal opportunities with all citizens to use the facilities of social, engineering and transport infrastructure, which will increase their individual mobility with the highest possible degree of independence.
7. A package of tender documentation is formed on the basis of the adopted program. The customer of the regional program is the Government of the Omsk Region, the executive coordinator is the Ministry of Labor and Social Development of the Omsk Region, the contracting organizations are determined by competitive selection. There are certain risks that must be foreseen in advance, for example, non-fulfillment of the contract on time, poor quality of work, etc. The criteria for competitive selection may serve as a tool to minimize them. In addition to the mandatory requirements, it is advisable to lay certain guarantees on the part of contractors. The customer, in turn, must ensure timely financing.
8. The implementation of accessibility requirements is carried out by the methods of new construction or reconstruction of existing facilities, through the acquisition of adapted rolling stock and equipment. Moreover, all decisions should be simple, recognizable, high-quality, durable, reliable and made in the same style that needs to be developed. In this regard, the tasks
should include a scientific component - this is a study of accessibility problems, which may include the development of accessibility criteria and measures to ensure them, training of specialists in a barrier-free environment, participation in the development of projects, technologies, selection of materials, decor elements, architectural elements, color schemes, fonts, sound support, accounting for the principles of universal design, etc.
9. Even if the target program is developed and adopted, its high-quality implementation requires great efforts from its customer-coordinator (directorate). Abroad, for these purposes, Project Management technology is used, a project team is formed. As a rule, a serious program is a series of interconnected projects, the management of which is coordinated to achieve benefits and a degree of manageability that are not available when they are managed separately. Project management technology provides for an analysis phase, including identifying participants, their key problems, obstacles and opportunities, clarifying cause-effect relationships, developing goals, identifying various strategies to achieve the goal, identifying common goals and objectives of the project. At the planning phase, the structure of the project is determined, its internal logic is checked, as well as the formulation of goals and results in measurable quantities, an approximate assessment of resources, the sequence and dependence of actions, the duration and distribution of responsibility are determined. In a market economy, any program or project is associated with investment and expected return. The team implementing the project is interested in its maximum effectiveness.
The most important element of the quality implementation of accessibility measures should be control by public disabled organizations, authorities and local self-government. Attracting people with disabilities by expert users allows you to step up the process of creating a barrier-free environment and avoid mistakes. It often happens that the project provides for accessibility measures, but in the process of its implementation are missed, or they do not meet the needs of people with limited mobility. In Moscow, for example, social protection departments have created departments for a barrier-free environment, which examine ready-made facilities for accessibility and where
coordination of projects, starting with a design assignment.
Due to the fact that investments in a comprehensive reconstruction to ensure accessibility are investments in real assets: in the development of land and territories, the construction and reconstruction of directly residential buildings, cultural amenities and transport infrastructure, it is difficult to calculate the social and economic effect of the program . In economic science, there are areas devoted to the national economy, production, management, ecology, individual branches and sectors of industry. Methods have been developed that allow one to determine the effectiveness of reducing harmful emissions, from switching to innovative farming methods, from introducing advanced technologies, etc. However, there is no section that studies the processes associated with the efficiency of forming a barrier-free environment and assessing their impact on the economy. country. Disabled people are one of the most vulnerable categories of citizens due to not only their social status, but also limited opportunities. Nevertheless, fighting for their rights, they improve the quality of life, making the living environment not only affordable, but also comfortable for the entire population. The positive effect is amplified many times in all sectors of the economy.
Many countries with developed economies are already reaping the benefits resulting from the introduction of well-developed market strategies that target older tourists and people with disabilities. Studies show that a market created by older people is just waiting to open. The annual income of the hotel and restaurant business in the United States grew by 12% due to the implementation of the standards provided for by the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990. People with disabilities also represent a rich source of untapped potential for job creation. The economic consequences of unemployment are expressed primarily in the loss of part of the gross national product (GNP). The American researcher A. Ouken calculated that every percent exceeding the unemployment rate reduces GNP by 2.5%. In our country, it is estimated that an increase of 1% in the number of working disabled people will increase revenues to the consolidated budget (including to the budget of the Pension
fund of the Russian Federation) by 1.5 billion rubles. In Europe and North America, the tourism market for people with disabilities and their partners is growing rapidly and is valued at billions of dollars. In Russia, for example, the implementation of the Sochi-Hospitable City project, taking into account accessibility for people with limited mobility, will allow not only the Paralympic Games to be held in 2014, but also millions of vacationers to use the accessible infrastructure of the city, which will lead to the development of industries related to tourism and services, employment and economic development throughout the region.
The significance of the barrier-free environment, taking into account financial and economic efficiency, is to: improve the quality of life of the entire population, reduce the time of temporary disability, increase the value of territories, reduce street injuries, organize walking and cycling, increase mobility and improve public health, increase employment of people with limited mobility, increase the quality of transport services, the integration of people with disabilities in society, an increase in budget revenues, an increase in the cultural level, ie consumer spending, business revenue growth and commercial structures, ultimately, leads to increased availability of regional economy.
Using these approaches will increase the efficiency of the process of accessibility formation and will improve the quality of life of the entire population to the level of international standards. Implementation of the state program “Accessible Environment” throughout the country using new project management technologies is, of course, an innovative way of developing the economy.
1. Federal target programs. -
iK: http://fcp.vpk.ru (accessed date:
2. Signature and ratification of the Convention and the Protocol / Rights and dignity of persons with disabilities // UN. - IK: http://www.un.org/russian/dis-abilities/countries.asp?navid\u003d23&pid\u003d612 (accessed: 03/27/2011).
3. Voskolovich N. A. Economics, organization and management of the public sector: a textbook for high schools / ed. N.A. Voskolovich. - M.: UNITY-DANA, 2008 .-- 367 p.
4. Safronov K. E., Leonova L. S. Program approach to the formation of a barrier-free environment // Labor and Social Relations: a scientific journal of the Academy of Labor and Social Relations. - 2010. - No. 8 (74). - S. 128-133.
5. Safronov K. E. Efficiency of the organization of transport services for the disabled in cities: monograph. - M.: DIA, 2010 .-- 208 p.
6. Safronov K. E. Methodological foundations for the formation of an accessible environment of cities and regions // Issues of planning and development of cities: materials of the XVI International scientific and practical. conf. / ed. prof. Yu. V. Kruglova, Assoc. V.S. Glukhova. - Penza: PGUAS, 2009.-S.50-53.
7. Safronov K. E. Management of the formation of a barrier-free environment in cities and regions of the Russian Federation // Economics. Entrepreneurship. Environment: international magazine. - 2010. - No. 3 (43). - S. 23-30.
8. Safronov K. E. Town-planning methods of forming a barrier-free environment // ASABBM1A. Architecture and Construction: A peer-reviewed scientific journal. - 2011.-№ 1.- S. 71-75.